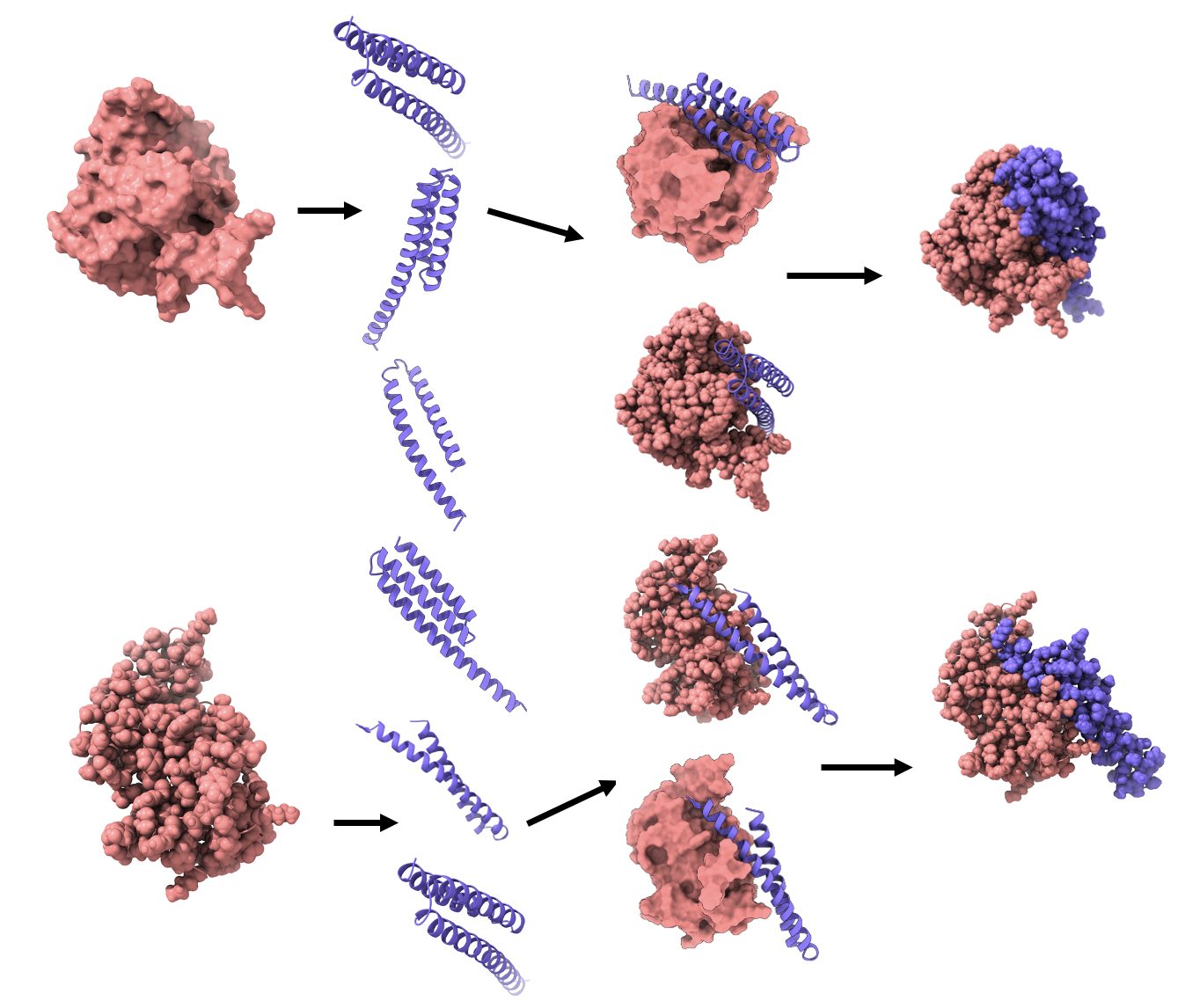
Peptide discovery
A peptide is a biologically active oligomer composed of two or more amino acids linked together by peptide bonds (covalent bonds formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another).
Peptides generally range from 2 to approximately 100 amino acids in length. Beyond this length, the structure is typically classified as a protein. The specific sequence of amino acids within a peptide, known as the primary structure, dictates its functional properties and biological activity, including roles in signaling, enzymatic activity, and structural functions in biological systems.
Peptides can be used naturally or also be optimized using engineering cycles. Nisin is one of Bota's major products. It is a polycyclic antibacterial peptide produced by the bacterium Lactococcus lactis that is used as a food preservative. It has just 34 amino acid residues!
We employ AI techniques to design peptides that can bind to specific targets. We can also check the interaction of any peptide with a specific target. This is useful when considering which peptides might have biological efficacy. This has proven useful for applications in hair and skin care.